What it is?
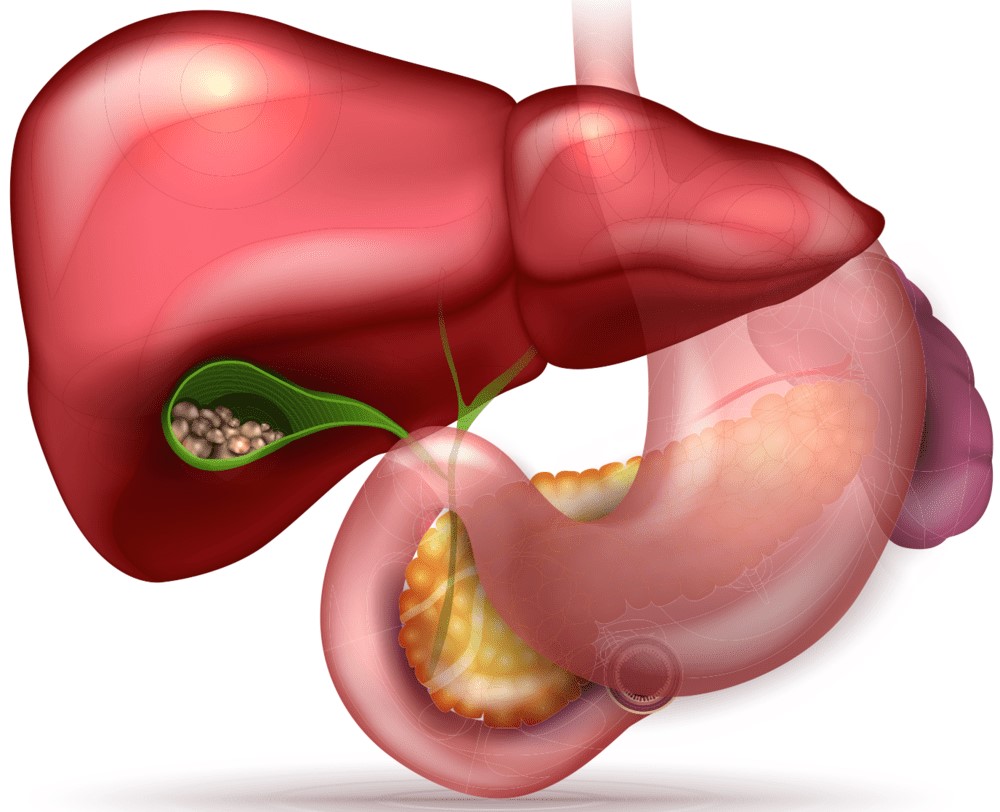
Gallstone disease (GSD) is a condition in which stones form in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
ZhKB occurs quite often. Ultrasound examination of practically healthy adults in 10-15% of them reveals stones in the gallbladder. More often women are ill.
Causes
Two main factors are to blame for the formation of stones: stagnation of bile in the gallbladder and an increase in the concentration of salts in bile due to metabolic disorders.
Stones can be triggered by: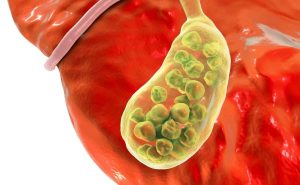
overeating, starvation, irregular eating, lack of dietary fiber;
sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work;
pregnancy;
taking hormonal contraceptives;
obesity;
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
What’s happening?
The formation of stones in the gallbladder occurs as a result of the deposition of crystals in oversaturated bile. The stones are composed of cholesterol, bilirubin and calcium salts. Gallstones interfere with the normal functioning of the gallbladder, and sometimes, moving to the mouth of the bile duct, clog it. As a result, the outflow of bile from the bladder is disrupted, its walls are overstretched and the person feels severe pain. In addition, the gallbladder can become inflamed. Over time, the gallbladder cannot fulfill its function – the accumulation of bile.
How to recognize?
While the stones are small and calmly lie in the gallbladder, a person may not be aware of his illness.
Signs by which one can suspect a gallstone disease: heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth, nausea, belching. When the process has gone far, patients have attacks of biliary colic: in the right hypochondrium or in the upper abdomen there is a sharp pain. It may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief. The pains may not be very severe, go away on their own, but still this is a serious reason to consult a gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics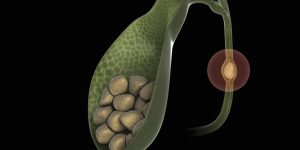
The diagnosis is made after examination and a series of examinations.
First of all, it is an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
In the most difficult cases, X-ray examination methods (cholangiography and cholecystography), computed tomography may be required.
Treatment
Therapeutic treatment consists in adhering to a diet https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diet_(nutrition) (excluding fatty, spicy, fried, that is, all choleretic products), taking antispasmodic drugs.
It is possible to dissolve small cholesterol stones with ursodeoxycholic acid preparations. The course of treatment is a year or more. Relapses are possible.
Surgical treatment is most appropriate. It is ideal to carry out a planned operation before recurrent seizures, in the absence of complications. It consists in removing the gallbladder, which can be done in two ways: classical cholecystectomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The type of operation is chosen by the surgeon.